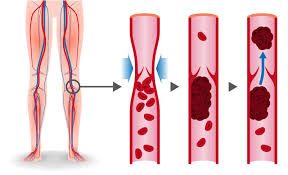
Veins and Arteries: Embolism
Embolism is a medical condition that can affect both veins and arteries. It occurs when a blood clot, called an embolus, forms and travels through the bloodstream, blocking a blood vessel at a different location from where it initially formed. This can lead to serious complications. Here is some information about embolism in veins and arteries:
Venous Embolism: Venous embolism refers to the formation of a blood clot, typically in the deep veins of the legs (deep vein thrombosis or DVT), which then dislodges and travels to other parts of the body. The clot can get stuck in the pulmonary arteries, causing a condition called pulmonary embolism (PE), which affects the lungs. Symptoms of PE may include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid heart rate, and coughing up blood. Prompt medical attention is essential for diagnosing and treating venous embolism.
Arterial Embolism: Arterial embolism occurs when a clot or other debris, known as an embolus, blocks an artery, interrupting blood flow to the organs or tissues supplied by that artery. This can lead to severe consequences depending on the affected area. For example, an embolism in a coronary artery can cause a heart attack, while an embolism in a cerebral artery can result in a stroke. Symptoms of arterial embolism may include sudden pain, pallor, coolness, weakness, or loss of function in the affected limb or organ. Immediate medical attention is crucial to minimize damage and restore blood flow.
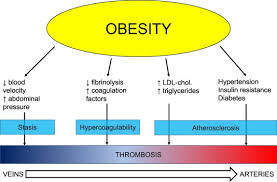
Risk Factors: Certain factors can increase the risk of developing embolism, such as:
- Prolonged immobility, such as during long-distance travel or bed rest after surgery.
- Obesity and a sedentary lifestyle.
- Smoking and tobacco use.
- Underlying medical conditions like cardiovascular disease, cancer, or inflammatory disorders.
- Pregnancy and postpartum period.
- Hormonal medications, including oral contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy.
- Advanced age.
- Inherited blood clotting disorders.
Prevention and Treatment: Prevention and treatment strategies for embolism may include:
- Physical activity and regular exercise to improve blood circulation.
- Maintaining a healthy weight and lifestyle.
- Avoiding prolonged immobility; if unavoidable, taking frequent breaks and performing leg exercises during long periods of sitting or lying down.
- Using compression stockings as recommended by healthcare professionals.
- Taking prescribed anticoagulant medications to prevent blood clot formation.
- In some cases, surgical interventions or procedures may be necessary to remove or dissolve the clot or to restore blood flow.
If you suspect you have an embolism or experience any symptoms related to embolism, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. The healthcare provider will conduct appropriate diagnostic tests and determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the specific situation.
Please note that this information is for general awareness and educational purposes only. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance regarding embolism and related medical conditions.



No comments:
Post a Comment