I believe you might be referring to "anticoagulants" rather than antibiotics when discussing the topic of heart embolism. Anticoagulants, also known as blood thinners, are medications commonly used in the management and prevention of conditions such as heart embolism or blood clots. However, it's important to clarify that I can provide general information, but it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for specific advice regarding your medical condition.
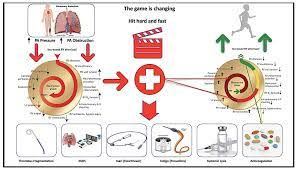
Heart embolism occurs when a blood clot or other material, such as a piece of plaque or a tumor, travels through the bloodstream and becomes lodged in an artery supplying blood to the heart. This can lead to an interruption of blood flow, resulting in various heart-related complications.
Anticoagulants are used to prevent the formation of blood clots or to keep existing blood clots from growing larger. They work by interfering with the clotting factors in the blood, reducing the ability of the blood to clot. This helps to prevent clot formation or reduce the risk of further complications from existing clots.
Commonly prescribed anticoagulants include warfarin, heparin, and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) such as rivaroxaban, apixaban, and dabigatran. The choice of anticoagulant depends on various factors, including the individual's medical history, the type of heart embolism, and other considerations.
It's important to note that anticoagulants are potent medications that require careful monitoring and adherence to prescribed dosage. Regular blood tests may be necessary to assess the effectiveness and safety of anticoagulant therapy. It is essential to follow the instructions of your healthcare provider and report any unusual symptoms or concerns promptly.
If you have specific questions or concerns regarding heart embolism or anticoagulant therapy, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance



No comments:
Post a Comment